What Is Lean Manufacturing ?
Sign up for our weekly newsletter for updates, articles and free giveaways of case studies, templates and training materials every issue! Simply enter your e-mail on the right
Here Is a Basic Lean Manufacturing Definition ...
People often ask the question " What is Lean Manufacturing ?" Lean should be recognised as a totally different way of looking at manufacturing. It’s about attacking waste; the massive areas in the value stream (manufacturing process), from raw material to finished goods, where no added value is taking place.
‘Lean thinking’ first appeared in the 1920s Henry Ford used it to improve his manufacturing flow lines while producing his famous Ford model T.
He used it to rid his company’s production lines of all waste, be it an activity or other form of waste, so he could meet his vast order schedule. Lean carried on in its infant form up to the seventies, where the global oil crisis demanded that petrol-guzzling engines, (that Ford had become used to making), be replaced by economical smaller engines.
This is when lean was adopted by Japan and the Toyota car company. Here it was refined to the present standard we are accustomed to.
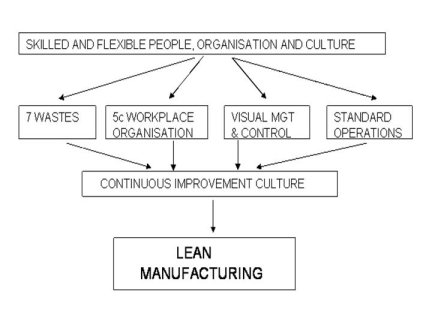
So what is lean manufacturing ? As already stated it’s the removal of waste from our business, but what do we class as waste.
There are seven wastes and they are as follows;
OVERPRODUCTION
e.g. making it for the sake of it
INVENTORY
e.g. high raw material stocks
WAITING
e.g. long set ups and times
MOTION
e.g. walking lifting putting down
TRANSPORTATION
e.g. unnecessary movement / extra handling
REWORK
e.g. customer satisfaction / right first time
OVERPROCESSING
e.g. fresh air cutting / speeds and feeds
But just removing waste only is not enough, so that’s where the other lean principles come into practice.
They cover all aspects of production in any environment and can be used by anyone who wants to improve his or her working environment and production processes.
Lean Consists of the following Elements...
What is Lean Manufacturing ?
LEAN THINKING AIMS
QUALITY
Built in quality
Zero defects / PPM
Route cause analysis
Everybody involved
COST
Increased capacity
Capital spend reduction
Optimised inventory level
Productivity increase.
DELIVERY
Drumbeat manufacture
Reliable and consistent
Responsive to fluctuation Lowest possible lead-time
TRADITIONAL FOCUS:
WORK HARDER FASTER FOR LONGER
LEAN APPROACH:
IMPROVE THE PROCESS TO ELIMINATE WASTE AND TO WORK SMARTER / SAFER
And always remember, without standardisation there can be NO improvement.
This is the basic building block of all improvement activities, so if you are asked what is lean manufacturing, always start with this.