Problem Solving
Problem solving can take many forms but, if you try to solve your problem without any structure, you may end up with a bigger issue than you started with !.
Definition of Problem :
Something that needs a solution.
Can be either positive or negative.
Frequencies:
• Chronic - Ongoing and Accepted problems
• Spasmodic - Sudden change to normal process.
Problem Levels
Level 0 - Abnormality only affecting those directly related to the process and contained.
Level 1 - Abnormality that affects the processes ability to achieve Q,C and D.
Level 2 - Abnormality that affects the next process and may have an impact on the final customer.
Level 3 - Abnormality that has affected the final customer.
Analysis of Problems
Qualitative tools
• Tools which are used to obtain and structure ideas during the cycle
Flow chart
5 why
Brainstorming
Cause & effect diagram (Ishikawa, fishbone)
Quantitative Tools
• Tools that are used to gather and analysis numerical data during the cycle.
Checksheets
Pareto
Control charts
Histograms
Scatter diagrams
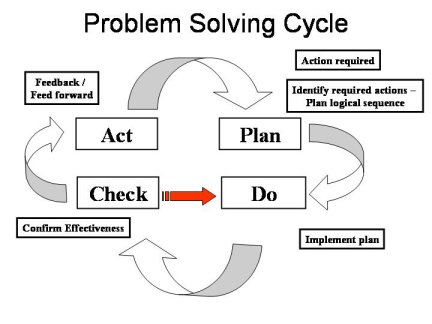
The 5 Principles :-
• Problem Definition
• Identify Root Cause
• Customer Protection and Countermeasure(s)
• Confirm Effectiveness of Countermeasure
• Feedback / Feed forward
The different types of problem solving
Preventative:
• This looks at putting in place solutions prior to abnormalities occurring. Best identified during the design stage prior to transfer to manufacturing using Advanced Quality Tools.
Pro- active:
• This looks at the current standards and by analysing data using the 7 quality control tools seeks to make kaizen improvements.
Reactive:
• This looks at the abnormalities that have occurred and by gathering and analysing data using some of the 7 quality control tools aims to provide a customer protection and countermeasure .