Overview of Six Sigma
This overview of Six Sigma is a brief explanation of the basic concepts, meant as a quick reference guide.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma is an effective business process improvement methodology.
It is not the Business of Quality.
It is the Quality of Business
It focuses on customers needs.
Customers can be:
external
internal
Six Sigma was developed at Motorola. It has since helped a number of world-class organizations, including General Electric, become more cost-competitive while achieving strong growth.
Why do Six Sigma?
Make us meet our customers increasing expectations
Boost our growth in line with that of our core customers
Enhance the value of the Company
Provide a consistent methodology of improvement
Six Sigma definitions
Sigma measures how far a process or product deviates from a target goal.
One Sigma = high variance from the goal (many defects)
Six Sigma = low variance from the goal (few defects)
In other words:
Six Sigma = 3.4 defects per million opportunities
Four Sigma = 6,210 defects per million opportunities
Three Sigma = 66,807 defects per million opportunities
Six Sigma is -
a statistical bench mark
sigma stands for variance of a measurable characteristic
The overview of Six Sigma improvement methodology is DMAIC
Define
Identify the product or process to be improved and top few critical to quality (CTQ) customer requirements.
Measure
Quantify how the process performs today and set improvement goal
Analyze
Identify the input variables that affect the CTQ's the most
Improve
Determine solutions for controlling the key process input variables, quantify their impact and compare to goal.
Control
Implement process design modifications and standardization methods for maintaining the improved performance level over time.
Six Sigma is Data Driven..
Initial process performance is quantified to establish baseline.
Data collection is planned to ensure it is information rich and statistically significant.
Data is appropriately graphed to unveil information.
Inferences are made using sound sampling techniques.
Causes are verified with data.
Solutions are validated with data.
The Foundation of Six Sigma is Data-Based Decision Making
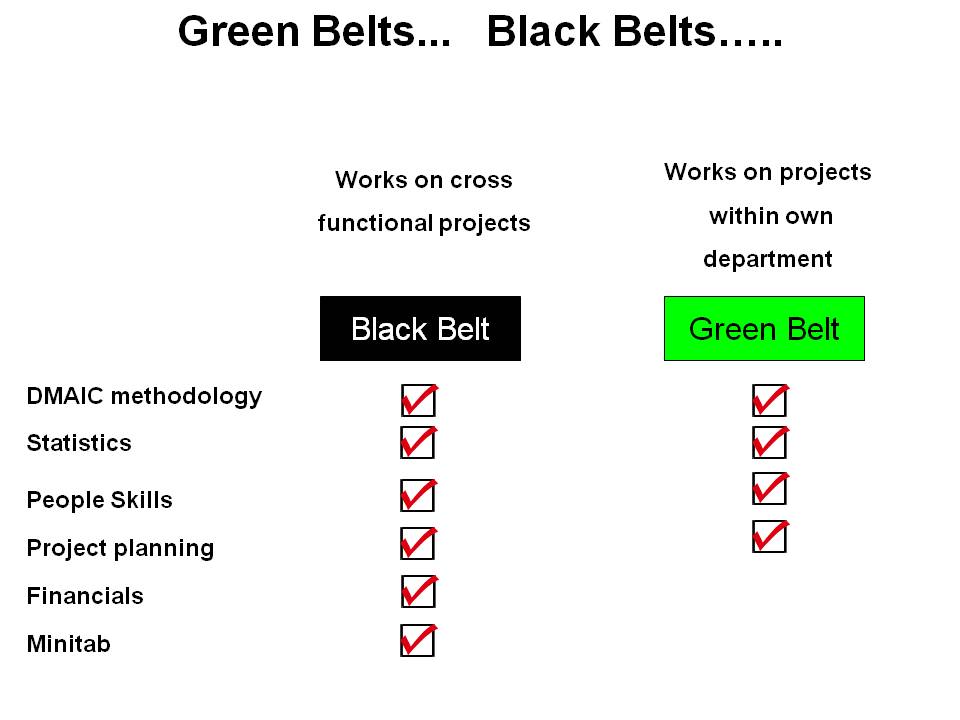
The key to six sigma implementation is the training and certification of green and black belts. For details of the easiest online method click this link -